How to You Know When You Have Reached True Root Cause?
Introduction
Before we motion to the field of study allow me share a curt story.
In one case during my bachelor days in a new boondocks, I went to see a dr.. I was running a loftier fever and was unwell for the last couple of days. Having examined me, he concluded it is Malaria. He prescribed some medicines and treated me. I was back on my anxiety and at piece of work within a couple of days.
I do not contract illnesses very ofttimes and usually do take skillful care of myself. Despite that, information technology came back in a calendar month's time. The doctor over again gave me some medicines and treated me. Once I was better, I asked him for advice on how to finish recurrence of the illness. The answer he gave was simple – keep your surround gratis from mosquitoes.
You would be thinking- that indeed is simple, why did I not realise that earlier. Well, happens in many situations!
I was seeking a cure for the symptoms earlier. To cease the recurrence, I had to place and remove the crusade.
To eliminate or solve a trouble, it is imperative to go to the root of the aforementioned. Go to the "Root Cause" and eliminate the problem.
What is Root Cause Assay (RCA)?
Let me take the above story and related analogy forwards.
The root crusade of the problem in the story was unhealthy surroundings almost my house. In one case I continue the surroundings clean, I eliminate mosquitoes. I stop or reduce recurrence of the disease.
Root cause analysis is the means to get to the underlying cause of the trouble.
Eliminate the root cause of the trouble, so you eliminate or reduce the recurrence of the trouble. This is where Root crusade assay concept and related tools are useful.
Why Root Crusade Analysis?
Today'southward fast-paced surround compels organizations to continually introduce. Innovate both on products and service offerings.
A leading organization running pizza chain outlets is a case in point. Growing at a steady pace, increasing geographical accomplish as well. Their concern - even loyal customers complaining about the quality of their production.
They conducted a review of the problem. They demand to increase the richness of the toppings used in their pop pizza offerings. I am one of their loyal customers. Having been to ane of their outlets recently, the look and taste of the revamped product surprised me. Did me and my family like the new offer – you bet!
It is not practiced enough to only await at problems and related causes at a high level. Earthworks down to place the root cause is hard work, just essential! Specially for organizations that are looking to improve continuously.
How to conduct Root Cause Analysis?
There are various tools bachelor for conducting Root Crusade Analysis process; we volition talk about information technology in particular after in this commodity.
Root Cause Assay steps are -
-
Define the problem
-
Ensure you identify the problem and align with a customer demand
-
If non existing, anticipate the problem from a customer perspective
-
What are the specific issues you observe
-
What happens if you do not tackle the trouble now – what is the business bear on
-
-
Collect data relating to the problem
-
Is at that place data to support the specific trouble
-
Speak to customers or employees if possible, seek their voice
-
Is it a recurring problem, how frequent in the past
-
What is the measurable impact of the problem on Fundamental Client Outcomes
-
-
Identify what is causing the problem
-
Identify the underlying cause
-
What is the gene or combination thereof leading to this
-
Identify as many causes as possible, practice non think of solutions at this stage
-
Involve your teams and relevant stakeholders
-
Use 5Y or Fishbone analysis, more than about it later
-
-
Prioritise the causes
-
Practice non tackle all at in one case, prioritise
-
PICK matrix is a good tool to achieve this
-
Comport in mind the impact and endeavour when you prioritise
-
Technology might be a key differentiator at this stage
-
-
Identify solutions to the underlying trouble and implement the change
-
Focus is on eliminating the trouble so it does non recur
-
Who volition implement the change and by when
-
Who is responsible to monitor and command the new procedure
-
What is the method and frequency of reporting performance
-
-
Monitor and sustain
-
Defining a solution is not plenty, execution is the key
-
Embed the new process within the existing business concern processes
-
Ensure the bear upon of the improvements are monitored and sustained
-
The process above defines at a simplistic level how Root Crusade problem solving blends into the operational excellence culture. The awarding may differ depending on the criticality of the problem.
Root Crusade Analysis Methods
Root Cause Assay is a simple technique performed with the objective of understanding the crusade of the trouble.
At that place are some popular tools in use. Let's sympathize each of them.
ane. 5 Why Analysis
Very simply described, this technique is about asking "Why?" five times or more than. Objective is to arrive at the underlying root cause to the problem.
Figure one
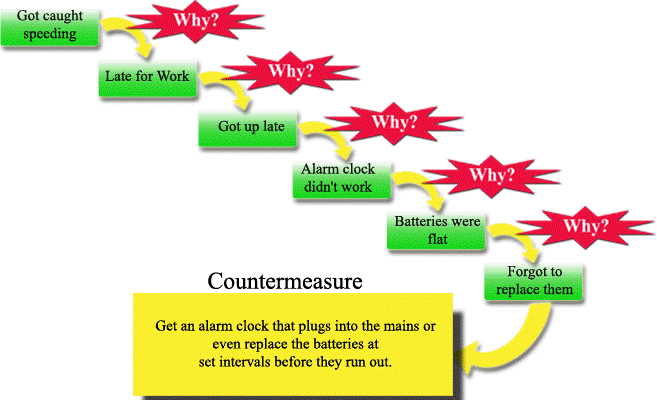
Paradigm source - http://www.educational-business-articles.com/5-whys/
A simple problem of over-speeding resolves by replacing the alarm clock. Or being more disciplined nearly changing the batteries.
Now, replace this in a business scenario for a accept-away restaurant.
A delay in food delivery might be due to traffic snarl. The underlying cause might exist a faulty appliance in the kitchen.
In either example, this tool is important since it focuses on the root cause of the problem. It seeks to eliminate the same and then the trouble does non recur.
2. Fishbone or Ishikawa Diagram
Ishikawa Diagram is named later Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa. Dr. Ishikawa developed a simple method of displaying the causes of a problem. This diagram went on to be known as the Ishikawa or Fishbone or Crusade & Effect Diagram.
The steps to depicting cause and issue on a Fishbone diagram are-
-
Define your problem
-
Brainstorm with the team on possible causes for the problem
-
Utilize the 6 Ms while doing so
-
Man – people performing the procedure or involved
-
Automobile – equipment and tools used within the process
-
Method – procedures followed
-
Material – Inputs required within the process
-
Measurement – data on input or product specifications
-
Mother nature – environment in which men and machines operate
-
-
Categorise all the causes as per the 6Ms
The last depiction would look like the figure beneath. Equally you tin see from Figure ii, it looks like a Fishbone, and that'south why the name.
Figure 2
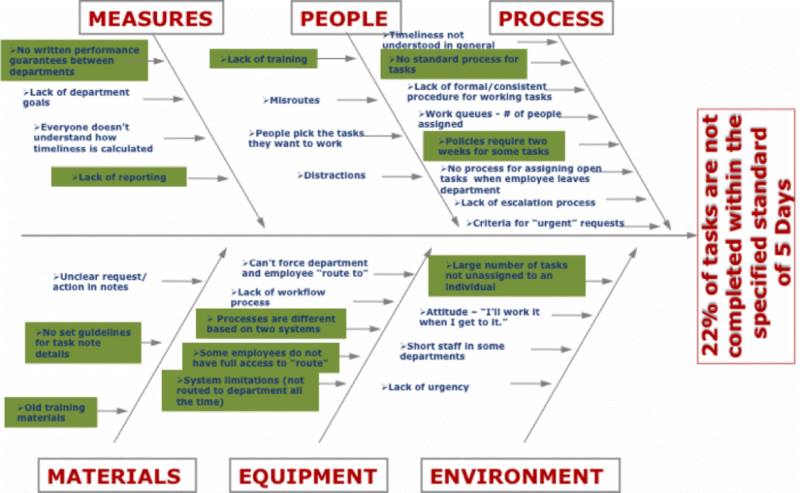
Epitome source - https://goleansixsigma.com/achieving-a-19-improvement-in-response-time-using-a-cause-and-effect-diagram/ -
Prioritise basis data and squad view. In the higher up diagram, the team believes the highlighted causes are the major contributory factors.
-
Brainstorm solutions for the prioritised causes and implement
The Fishbone or Cause & Upshot Diagram is an impactful tool. It represents all possible causes and prompts the squad to retrieve from a 6M perspective.
There are other variations to the 6M.
Some manufacturing companies use 4M (Human being, Motorcar, Material, Method). While some service companies employ 8P (Physical Evidence, People, Identify, Service, Price, Promotion, Procedure, Productivity and Quality).
iii. Pareto Analysis
Pareto assay is based on the principle that "lxxx% of the effects come from 20% of the causes". To put it differently, "20% of the work creates 80% of the results". This is also chosen the "80/xx" dominion.
Look at it either way – the focus is on the "vital few" equally opposed to the "piffling many".
Whatsoever problem that we start reviewing, you would experience a tendency to move towards the trivial causes. Our energies demand to focus on the "vital few" be it from a problem solving or commitment perspective.
Management consultant Joseph M. Juran suggested the principle. He named information technology after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist. While at the University of Lausanne, Pareto noted the 80/twenty connection. He showed that 80% of the land in Italia was owned by 20% of the population.
Steps to acquit a Pareto analysis are-
-
Define categories or classifications for the causes
-
Collect data from historical sources or collect data through logs
-
Assign a time period for which the data pertains to or to be collected
-
Calculate the number of occurrences or observations for each of the categories
-
Convert the numbers into percent of total
-
Sort the data by numbers, largest to smallest
-
Compute cumulative percentages
-
Draw a graph using Minitab or Microsoft Excel
Let's take the case of an Insurance Premium collections process. The problem is high number of queries sent back by clients on invoices raised. The impact is delayed premium collection.
Data tabular array as follows-
| ABC Insurance - Premium collections | |||
| Number of customer queries by category | |||
| Period - Jan '17 - Dec '17 | |||
| Category | Number | %age | Cumulative %age |
| Insufficient backup bear witness | 115 | 33% | 33% |
| Tax computation mismatch | 101 | 29% | 62% |
| Incomplete documentation | eighty | 23% | 85% |
| Commission rate mismatch | 40 | 11% | 96% |
| Other | 14 | iv% | 100% |
| 350 | |||
The pareto chart every bit displayed in a graph (using excel) looks as in Figure 3.
Effigy 3
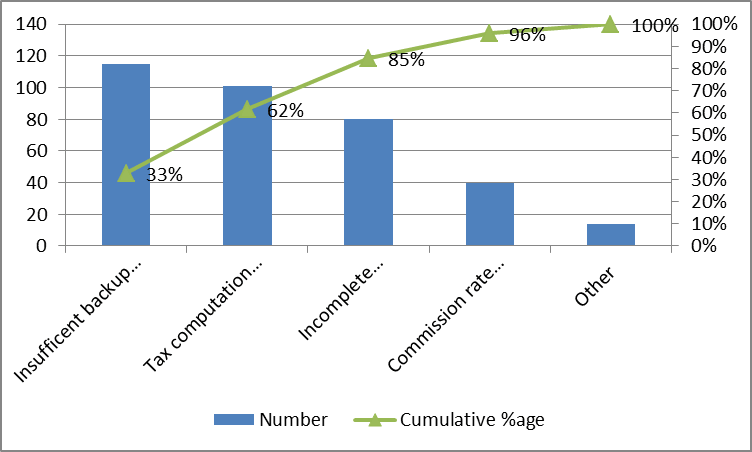
Equally per the Pareto chart in Effigy 3, 85% of the causes for delayed premium collections due to queries are –
-
Insufficient backup evidence
-
Tax computation mismatch
-
Incomplete documentation
-
Equally a team, the focus would be on eliminating or reducing these queries, thereby, positively impacting collections.
4. Brainstorming
Equally a RCA tool, this is ane of the simplest to understand; almost difficult to apply.
Brainstorming is getting all the concerned team members into a room. Objective is to understand possible causes to the trouble. Focus on solutions only once primary causes are identified.
The procedure steps are-
-
Kicking off past champion, attended by process owner, projection team, SMEs and Half dozen Sigma team
-
Review the trouble defined
-
Find all possible causes to the problem – hand post-its to attendees and request individual views (no discussions)
-
Apply 6M to stimulate possible causes
-
Categories the causes using Affinity diagram (Figure iv)
-
Prioritise the causes, discuss and shortlist possible solutions via voting and group consensus
-
Review of shortlisted solutions past Champion for buy-in followed past next steps for subsequent inquiry
-
List of farther form of action, Minutes of meeting distributed
Brainstorming can generate effective results. In contempo times, Encephalon-writing has evolved as a tool too.
It is a reformed version of Brainstorming. The focus is on private view- points initially (at both causation and solution phase).
Effigy 4

In a nutshell
Six Sigma popularly gets perceived as a techy infinite. The reality is – simplistic tools similar Root Crusade Assay blends into the operational excellence culture effectively. It is a common sense approach to problem-solving.
Hope you liked reading this article. Feedback through the discussion forum link. Allow me know in case you demand whatever further information on any of the concepts by commenting here.
Find more than tools to improve your efficiency – Get Certified Now!
williamslitis1955.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.greycampus.com/blog/quality-management/how-do-you-determine-the-root-cause
0 Response to "How to You Know When You Have Reached True Root Cause?"
Post a Comment